It is important to decarbonise cities because the cities which more than half of us live account for nearly two-thirds of the CO2 emissions that lie at the root of our planet’s looming climate crisis. Skyscrapers in megalopolises, shopping malls, SUVs in the streets, air conditioners in a growing number of places throughout the globe – all consume a vast amount of high CO2-content energy.
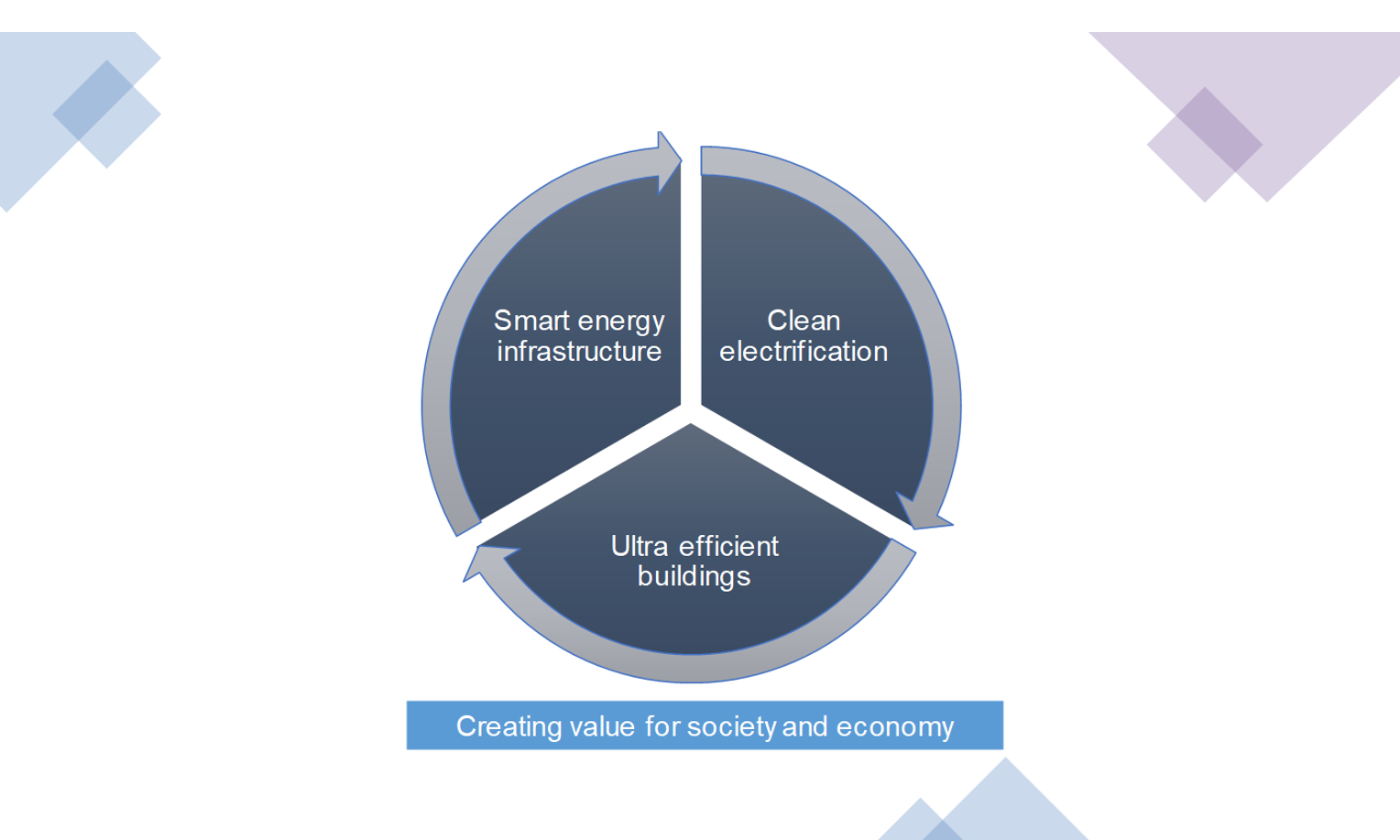
How do we decarbonise cities? leveraging clean electrification and digital technology to harmonize urban energy systems, while also thinking beyond individual projects to consider their impact within the surrounding communities and the built environment.
Also read: Can the built environment and fashion influence others towards an environment-centered approach to doing business?
In fact, urban energy, transport and building infrastructures are gradually becoming greener: There are more electric vehicles on city streets, better water treatment and recycling schemes, and more solar panels on rooftops around the globe. According to International Energy Agency estimates, renewables like solar and wind are set to become the largest source of electricity generation worldwide by 2025, supplying one-third of the world’s electricity and ending coal’s decades-long dominance of the global power mix.
All this is, of course, welcome.
But with climate change accelerating, we need more comprehensive decarbonization actions on three fronts. First, we need even more energy to come from renewable sources. Second, we need more cars, heating and other activity to be powered by clean electricity. Third, we need everything from factories, to office buildings, homes, transport systems and consumer devices to become more energy-efficient.
This third lever might not as headline-grabbing as the rise of solar panels or electric vehicles. But it is a big piece of the decarbonization puzzle, with an even larger potential enabled by digital technologies.
Consider, for example, the technologies that make buildings more energy-efficient, by automatically adapting the amount of cooling, heating or lighting to occupancy levels at any given moment. Or digital tools that allow the operators of a manufacturing site in Sweden or a public utility in India to run their operations or distribution systems more efficiently and even remotely, rather than in person (a feature that has proved critical in these times of social distancing and lockdowns).

Comments
Post a Comment